Oxidation Number of Chlorine
Electronegativity Pauling scale The tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself expressed on a relative scale. Table of Element Valences.

How To Find The Oxidation Number For Cl In Cl2 Chlorine Gas Youtube
In pool water chemistry once added to the water all chlorine oxidizers including salt produce hypochlorous acid HOCl hypochlorite ions OClᐨ and a byproduct specific to the type of.

. Chloride ionCl electron configuration. Therefore the valency of chlorine is 7. Chlorine is a chemical element with atomic number of 17 and molecular mass of 355.
The oxidation number of any atom in its elemental form is 0. Disinfection time for several different types of pathogenic microorganisms with chlorinated water containing a chlorine concentration of 1 mgL 1 ppm when pH 75 and T 25 C. Due to this the oxidation states of chlorine are 7 5 1 and -1.
Dichlor is a fairly common type of chlorine in the industry but its one that comes with a number of strings attached that ultimately make it difficult to recommend to most pool owners. At higher pH levels in the water chlorine becomes less effective and loses much of its oxidation potential requiring more chlorine or non-chlorine oxidizers to reach the same ORP levels. Assign oxidation numbers to the elements of the following compounds using the.
Values are given for typical oxidation number and coordination. The lower the pH the higher the proportion of Hypochlorous Acid HOCl to Hypochlorite Ion OCl- and the higher the ORP. Increased chlorine level allows contaminants to accumulate and pollute the water.
C 6 H 4 CL 2. Free chlorine when used for disinfection forms when chlorine gas is dissolved. Here are a few that are most common in swimming pools.
The oxidation number of fluorine is always 1. This is determined based on the number of electrons that would be added lost or shared if it reacts with other atoms. In chemistry the oxidation state or oxidation number is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionicIt describes the degree of oxidation loss of electrons of an atom in a chemical compoundConceptually the oxidation state may be positive negative or zero.
Chloride ionCl electron configuration107 Oxidation Reactions of Alkenes Organic Chemistry Ihttpskpupressbookspuborganicchemistrychapter10-7-oxidation. Chlorine is the second member of halogen group it has similar properties like fluorine bromine and iodine. Disinfection time for several different types of pathogenic microorganisms with chlorinated water containing a chlorine concentration of 1 mgL 1 ppm when pH 75 and T 25 CDichlor.
It also means that the compound will be readily available. The chlorine atom in chlorine dioxide has an oxidation number of 4. The oxidation number is the hypothetical charge of an atom in a molecule or ion and it is a measure of its apparent capacity to gain or lose electrons within that species.
Redox reductionoxidation ˈ r ɛ d ɒ k s RED-oks ˈ r iː d ɒ k s REE-doks is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Molecular weight 12019 g. This is more than 25 times the oxidation capacity of chlorine.
The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is 0. In addition the peroxy radicals from the OH reaction can form N-2-formylphenylformamide C 8 H 7 NO 2 for the first time providing evidence for the chemical. For example CaH 2 its oxidation number equals to 1.
Should You Use This Type of Chlorine in Your Pool. Osmium tetroxide OsO 4 is a widely used oxidizing agent for such purposePotassium permanganate can be used as well though further oxidation is prone to occur to cleave the diol because it is a stronger oxidizing agent 1072What Is Valence or Valency in Chemistry. Naturally occurring it is found in the mineral form of sodium chloride common salt and other salts.
The sum of oxidation numbers added for different atoms in a compound should equal zero. This cloudiness is caused due to the pools reduced ability of oxidation. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state of a chemical or atoms within it.
From the above information we can say that chlorine exhibits variable valency. Valence is denoted using a positive or negative integer used to represent this binding capacity. Chlorine bromine and iodine usually have an oxidation number of 1 unless theyre in combination with oxygen or.
When we look at the molecular weight chlorine dioxide contains 263 available chlorine. Thus the valency of nitrogen is 3 whereas it can have oxidation numbers from -3 to 5. Difference between Valency and Oxidation Number.
C 9 H 12. Free chlorine has a high oxidation potential and is a more effective disinfectant than other forms of chlorine such as chloramines. Man-made chlorine is commercially manufactured through the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution.
Oxygen moles required for reaction 5. Electron affinity The energy released when an electron is added to the neutral atom and a negative ion is formed. The oxidation potentials of.
For this reason chlorine dioxide accepts 5 electrons when it is reduced to chloride. Instead consider trichlor tablets for a more hands off approach with less risk of overdosing your pool on stabilizer or liquid chlorine for a more manageable albeit manual. Furthermore it can lead to a pool that looks cloudy.
Furthermore it can lead to a pool that looks cloudy. For example common valences of copper are 1 and 2. Molecular weight 12019 g Pagination12NextSee more.
Molecular weight 14701 gmol. Reaction with Ozone C 9 H 12 CL 2 5 O 3---- 6C0 2 2 H 2 O CL 2 O. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a monatomic ion is equal to the overall charge of that ion.
OS is positive for halogens like chlorine iodine and bromine when combined with oxygen. Therefore the valency of chlorine is 1 3 5 and 7. First ionisation energy The minimum energy required to remove.
Oxidation potential is a measure of how readily a compound will react with another. Therefore the valency of chlorine is 7. 12-Dihydroxylation the conversion of the CC double bond to 12-diol is an oxidative addition reaction of alkene.
Factors that affect ORP. C 6 H 4 CL 2. 12-Dihydroxylation the conversion of the CC double bond to 12-diol is an oxidative addition reaction of alkene.
The OS of an ionic compound equals the ions charge when calculating it for polyatomic ions. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature many bonds exhibit strong. When iodine chlorine and bromine are combined with oxygen their oxidation number is positive.
Chlorine concentrations contact time temperature pH number and types of microorganisms concentrations of organic matter in the water. Herein we newly derived a kinetic model for trace-substance removal by catalytic reaction and applied it to the Mn 2 removal. This cloudiness is caused due to the pools reduced ability of oxidation.
Chlorine has electronic configuration Ne 3s23p5 with the seven electrons in the third outermost shell acting as its valence electrons. Table of Element Valences. When the oxidation number of the atoms of a compound are added together the.
Increased chlorine level allows contaminants to accumulate and pollute the water. Due to this the oxidation states of chlorine are 7 5 1 and -1. The increase in chlorine levels results in poor sanitation.
Therefore the oxidation mechanism of indole is distinct from that of previously reported amines which primarily form highly oxidized multifunctional compounds imines or carcinogenic nitrosamines. Fluorine and other halogens have an oxidation number 1 when they appear as halide ions in their compounds. Valence is denoted using a positive or negative integer used to represent this binding capacity.
Here chlorine has seven unpaired electrons. Molecular weight 14701 gmol. Chlorine levels and pH values are closely linked to each.
C 9 H 12. Therefore the valency of chlorine is 1 3 5 and 7. A number of water chemistry factors can affect your ORP.
Oxygen moles required for reaction 5. Osmium tetroxide OsO 4 is a widely used oxidizing agent for such purposePotassium permanganate can be used as well though further oxidation is prone to occur to cleave the diol because it is a stronger oxidizing agent 1072. For example common valences of copper are 1 and 2.
A high oxidation potential means many different compounds are able to react with the compound. Valency is different from the oxidation number and it has NO SIGN. Chlorine Explanation Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and it has atomic number 17.
From the above information we can say that chlorine exhibits variable valency. Reaction with Ozone C 9 H 12 CL 2 5 O 3---- 6C0 2 2 H 2 O CL 2 O. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state of a chemical or atoms within it.
Number of O 2 molecules consumed per molecule of compound 4. Catalytic oxidative removal of Mn 2 on activated-carbon surfaces by free chlorine was recently discovered and found to be potentially practicable for water treatment when using micrometer-sized activated carbon.

How To Find Oxidation Numbers For Chlorine Cl And Cl2 Youtube

An Introduction To Oxidation State Online Chemistry Tutor

Question Video Deducing The Oxidation State Of Chlorine In The Hypochlorite Ion Nagwa

How To Find The Oxidation Number For Cl In Cl2 Chlorine Gas Youtube
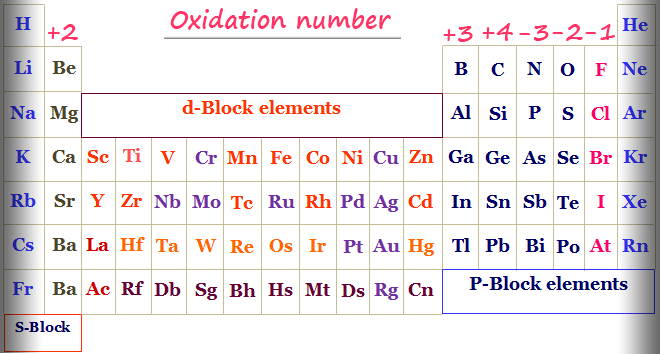
Oxidation Number Periodic Table Elements Definition Rules
Oxidation Number Of Oxygen Online 54 Off Www Wtashows Com
0 Response to "Oxidation Number of Chlorine"
Post a Comment